
Input latitude and longitude values or an sf/sfc POINT
object and get back the time zone in which they exist. Two methods are
implemented. One is very fast and uses Rcpp in conjunction with source
data from (https://github.com/darkskyapp/tz-lookup-oss/). However,
speed comes at the cost of accuracy - near time zone borders away from
populated centres there is a chance that it will return the incorrect
time zone.
The other method is slower but more accurate - it uses the sf package to intersect points with a detailed map of time zones from here.
lutz also contains several utility functions for helping to understand and visualize time zones, such as listing of world time zones,including information about daylight savings times and their offsets from UTC. You can also plot a time zone to visualize the UTC offset over a year and when daylight savings times are in effect.
You can install lutz from CRAN with:
install.packages("lutz")Or you can install the development version from github with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("ateucher/lutz")There are two functions in this package for looking up the time zones
of coordinates: tz_lookup() which works with both
sf/sfc and SpatialPoints objects, and
tz_lookup_coords for looking up lat/long pairs. Use the
method argument to choose the "fast" or
"accurate" method.
library(lutz)
tz_lookup_coords(49.5, -123.5, method = "fast")
#> [1] "America/Vancouver"
tz_lookup_coords(49.5, -123.5, method = "accurate")
#> [1] "America/Vancouver"
tz_lookup_coords(lat = c(48.9, 38.5, 63.1, -25), lon = c(-123.5, -110.2, -95.0, 130))
#> [1] "America/Vancouver" "America/Denver" "America/Rankin_Inlet"
#> [4] "Australia/Darwin"sf objects:library(sf)
library(ggplot2) # this requires the devlopment version of ggplot2
# Create an sf object out of the included state.center dataset:
pts <- lapply(seq_along(state.center$x), function(i) {
st_point(c(state.center$x[i], state.center$y[i]))
})
state_centers_sf <- st_sf(st_sfc(pts))
# Use tz_lookup_sf to find the time zones
state_centers_sf$tz <- tz_lookup(state_centers_sf)
state_centers_sf$tz <- tz_lookup(state_centers_sf, method = "accurate")
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = state_centers_sf, aes(colour = tz)) +
theme_minimal() +
coord_sf(datum = NA)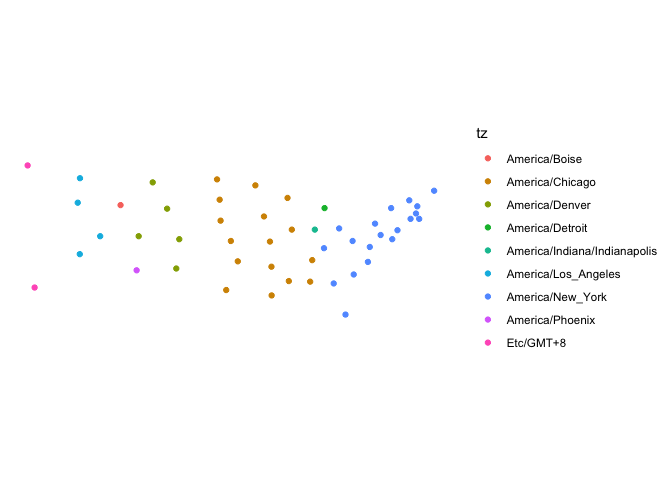
SpatialPoints
objects:library(sp)
state_centers_sp <- as(state_centers_sf, "Spatial")
state_centers_sp$tz <- tz_lookup(state_centers_sp)
ggplot(cbind(as.data.frame(coordinates(state_centers_sp)), tz = state_centers_sp$tz),
aes(x = coords.x1, y = coords.x2, colour = tz)) +
geom_point() +
coord_fixed() +
theme_minimal()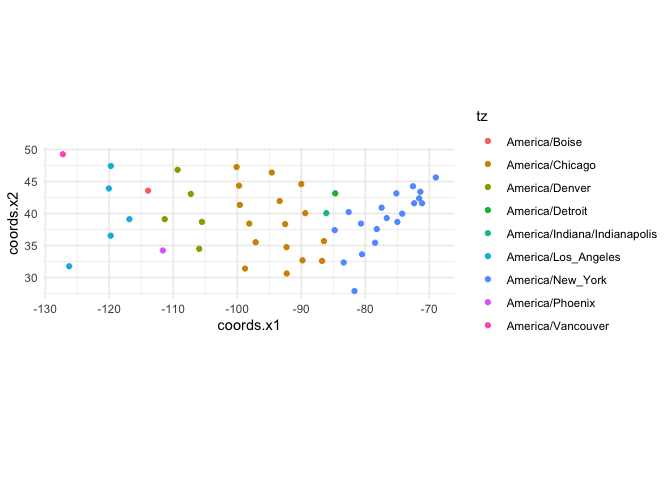
Note that there are some regions in the world where a single point
can land in two different overlapping time zones. The
"accurate" method includes
these, however the method used in the "fast" does not
include overlapping time zones (at least
for now).
We can compare the accuracy of both methods to the high-resolution
time zone map provided by https://github.com/evansiroky/timezone-boundary-builder.
This is the map that is used by lutz for the
"accurate" method, but in lutz it is
simplified by about 80% to be small enough to fit in the package.
## Get the full time zone geojson from https://github.com/evansiroky/timezone-boundary-builder
download.file("https://github.com/evansiroky/timezone-boundary-builder/releases/download/2019a/timezones-with-oceans.geojson.zip",
destfile = "tz.zip")
unzip("tz.zip", exdir = "data-raw/dist/")library(lutz)
library(sf)
library(purrr)
library(dplyr)
tz_full <- read_sf("data-raw/dist/combined-with-oceans.json")
# Create a data frame of 500000 lat/long pairs:
set.seed(1)
n <- 500000
ll <- data.frame(id = seq(n), lat = runif(n, -90, 90), lon = runif(n, -180, 180))
ll_sf <- st_as_sf(ll, coords = c("lon", "lat"), crs = 4326)
# Overlay those points with the full high-resolution time zone map:
ref_ll_tz <- sf::st_join(ll_sf, tz_full)
# Combine those that had overlapping time zones
ref_ll_tz <- ref_ll_tz %>%
st_set_geometry(NULL) %>%
group_by(id) %>%
summarize(tzid = paste(tzid, collapse = "; "))
# run tz_lookup with both `"fast"` and `"accurate"` methods and compare with
# the time zones looked up with the high-resolution map:
tests <- map_df(c("fast", "accurate"), ~ {
time <- system.time(test_ll_tz <- tz_lookup(ll_sf, method = .x, warn = FALSE))
comp <- ref_ll_tz$tzid == test_ll_tz
matches <- sum(comp, na.rm = TRUE)
mismatches <- sum(!comp, na.rm = TRUE)
list(
method = .x,
time = time["elapsed"],
matches = matches,
mismatches = mismatches,
accuracy = matches / (matches + mismatches),
ref_nas = sum(is.na(ref_ll_tz$tzid)),
fun_nas = sum(is.na(test_ll_tz))
)
})knitr::kable(tests)tz_plot()tz_plot("America/Vancouver")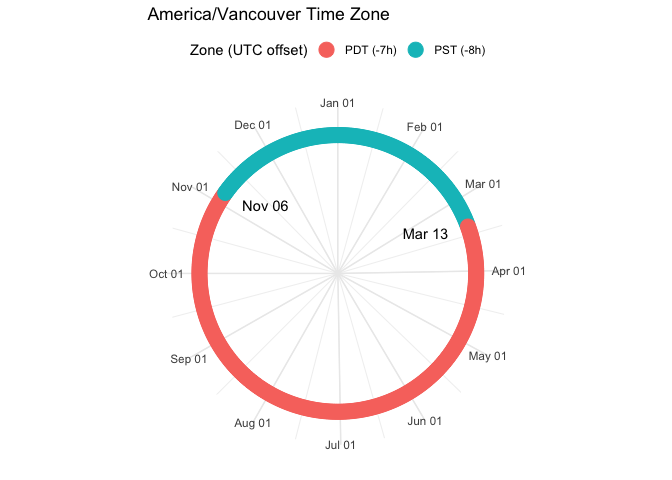
tz_offset()# A Date object
tz_offset(Sys.Date(), "Africa/Algiers")
#> tz_name date_time zone is_dst utc_offset_h
#> 1 Africa/Algiers 2023-10-17 CET FALSE 1
# A Date-like character string
tz_offset("2017-03-01", tz = "Singapore")
#> tz_name date_time zone is_dst utc_offset_h
#> 1 Singapore 2017-03-01 +08 FALSE 8
# A POSIXct date-time object
tz_offset(Sys.time())
#> Warning: You supplied an object of class POSIXct that does not have a time zone
#> attribute, and did not specify one inthe 'tz' argument. Defaulting to current
#> (America/Vancouver).
#> tz_name date_time zone is_dst utc_offset_h
#> 1 America/Vancouver 2023-10-17 12:11:11 PDT TRUE -7tz_list()tz_list() %>%
head(20) %>%
knitr::kable()| tz_name | zone | is_dst | utc_offset_h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Africa/Abidjan | GMT | FALSE | 0 |
| 2 | Africa/Accra | GMT | FALSE | 0 |
| 3 | Africa/Addis_Ababa | EAT | FALSE | 3 |
| 4 | Africa/Algiers | CET | FALSE | 1 |
| 5 | Africa/Asmara | EAT | FALSE | 3 |
| 6 | Africa/Asmera | EAT | FALSE | 3 |
| 7 | Africa/Bamako | GMT | FALSE | 0 |
| 8 | Africa/Bangui | WAT | FALSE | 1 |
| 9 | Africa/Banjul | GMT | FALSE | 0 |
| 10 | Africa/Bissau | GMT | FALSE | 0 |
| 11 | Africa/Blantyre | CAT | FALSE | 2 |
| 12 | Africa/Brazzaville | WAT | FALSE | 1 |
| 13 | Africa/Bujumbura | CAT | FALSE | 2 |
| 14 | Africa/Cairo | EET | FALSE | 2 |
| 16 | Africa/Cairo | EEST | TRUE | 3 |
| 17 | Africa/Casablanca | +01 | TRUE | 1 |
| 18 | Africa/Casablanca | +00 | FALSE | 0 |
| 19 | Africa/Ceuta | CET | FALSE | 1 |
| 20 | Africa/Ceuta | CEST | TRUE | 2 |
| 21 | Africa/Conakry | GMT | FALSE | 0 |